The Gilded Age, a popular TV series, boasts a remarkable cast of talented actors who bring the era to life. Fans of the show are often curious about the details of the cast members, including their heights and ages. In this article, we will explore some fascinating information about the Gilded Age cast and unveil their heights and ages.
Table of Contents
ToggleKey Takeaways:
- The Gilded Age cast is comprised of a diverse and talented group of actors.
- Knowing the heights and ages of the cast members adds an intriguing layer to the characters they portray.
- Stay tuned as we reveal the heights and ages of your favorite Gilded Age cast members!
- Understanding the physical attributes of the cast can enhance the viewing experience and bring a deeper appreciation for their performances.
- Discover more about the Gilded Age cast and immerse yourself in the captivating world of the show.
The Impact of the Transcontinental Railroad
The completion of the Transcontinental Railroad in 1869 had a profound impact on the United States, shaping its future in multiple ways. The development of this monumental railway system connected the eastern and western regions of the country, revolutionizing transportation and fueling economic growth.
One of the most significant effects of the transcontinental railroad was its contribution to the rapid settlement of the western regions. As the tracks extended across the vast expanse of the country, new towns and cities emerged along the route. The railroad provided people with easier access to the western frontier, attracting pioneers, settlers, and prospectors seeking opportunities in this vast, untapped land.

The expansion of the railroad also played a crucial role in facilitating the transportation of goods and resources across the nation. Previously, the transportation of goods relied heavily on slow and inefficient methods such as wagons and ships. The transcontinental railroad revolutionized this process, enabling faster and more efficient movement of goods from coast to coast. This newfound ease of transportation significantly impacted trade, commerce, and the overall economy of the United States.
The completion of the transcontinental railroad brought about economic prosperity, benefiting not only rail companies but also various industries connected to the railroad. As rail lines expanded, new markets opened up, providing opportunities for businesses to grow. Rail executives and investors amassed significant wealth, leading to the emergence of powerful railroad magnates during the Gilded Age.
The Economic Growth of the Gilded Age
The growth of the railroad industry acted as a catalyst for the broader economic growth experienced during the Gilded Age. The expansion of rail networks facilitated the movement of goods on a massive scale, spurring industrialization and trade. The transportation of raw materials, such as coal and iron, from remote areas to industrial centers became more efficient, stimulating the growth of industries and manufacturing.
The railroad expansion was pivotal to the prosperity of the Gilded Age. It connected the nation, accelerated settlement, and provided the infrastructure that enabled significant economic growth.
The construction and operation of the transcontinental railroad created employment opportunities for thousands of workers, both skilled and unskilled. It also attracted immigrants who sought employment in railroad-related industries. This influx of labor fuelled urbanization and population growth, leading to the rise of major cities across the country.
| Impact of the Transcontinental Railroad | |
|---|---|
| 1. Rapid settlement of the western regions | 5. Improved transportation of goods |
| 2. Boosted trade and commerce | 6. Economic growth and prosperity |
| 3. Emergence of powerful rail companies | 7. Job creation and urbanization |
| 4. Facilitated industrialization |
The impact of the transcontinental railroad cannot be overstated. It transformed the United States into a more interconnected and economically dynamic nation. The railroad expansion and the subsequent economic growth of the Gilded Age set the stage for significant societal change, illustrating the powerful relationship between infrastructure development, transportation, and economic prosperity.
Robber Barons and Industrialization
The Gilded Age saw the emergence of powerful individuals known as robber barons who played a significant role in shaping the era of industrialization. These wealthy tycoons, including Cornelius Vanderbilt, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie, amassed enormous fortunes and exerted control over various industries, often monopolizing them.
Robber barons prioritized their personal gain, using ruthless tactics to eliminate competition, consolidate power, and accumulate wealth. They employed methods such as vertical integration, horizontal consolidation, and aggressive pricing strategies to maintain control over their respective markets. With increasing influence and wealth, they rose to the status of industrial magnates, dominating sectors like railroads, oil, and steel.
Despite their reputations as ruthless businessmen, some robber barons also engaged in philanthropic activities, leaving behind a mixed legacy. Andrew Carnegie, for example, was known for his significant contributions to libraries, educational institutions, and cultural organizations, while John D. Rockefeller established the Rockefeller Foundation, focusing on initiatives related to education, medicine, and scientific research.
“The man who dies thus rich dies disgraced.” – Andrew Carnegie
Industrialization during the Gilded Age not only led to economic expansion but also contributed to societal and economic disparities. While the robber barons accumulated vast wealth, the working class faced harsh conditions, including long hours, low wages, and unsafe working environments. The rise of monopolies further exacerbated income inequality and limited opportunities for small businesses.
Ultimately, the robber barons and the era of industrialization shaped the economic landscape of the Gilded Age. Their pursuit of wealth and power had profound impacts on American society, both positive and negative. The legacy of these industrialists continues to provoke discussions about concentrated wealth, monopolistic practices, and the role of philanthropy in a capitalist system.

Influence of Monopolies
Monopolies established by the robber barons exerted immense influence over the American economy, often leading to negative consequences. With their ability to control prices and eliminate competition, monopolistic practices hindered innovation, limited consumer choice, and stifled entrepreneurship. The unchecked power of these industrial giants raised concerns about fair market practices and the concentration of power in the hands of a few.
The Push for Regulation and Antitrust Laws
The rise of robber barons and their monopolistic practices sparked public outcry and paved the way for regulatory reforms. Progressive leaders such as Theodore Roosevelt and Woodrow Wilson championed antitrust measures to curb the power of monopolies and promote fair competition. The Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, for instance, aimed to prevent monopolistic practices and protect consumers from unfair business practices.
Corporate Philanthropy
While the robber barons’ ruthless business practices drew criticism, they also engaged in philanthropic endeavors. By donating significant portions of their wealth to charitable causes, they sought to shape public opinion, gain social acceptance, and address some of the social issues perpetuated by the Industrial Revolution. However, the debate over whether their philanthropy served as genuine altruism or merely a form of public relations activity persists to this day.
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution
The Gilded Age marked a significant period of industrial revolution in America, bringing about a transition from an agrarian society to an industrialized one. This transformation had far-reaching effects, including urbanization, the growth of labor unions, and the exacerbation of poverty and inequality.
As industries flourished and technology advanced, cities emerged as centers of economic activity, leading to a rapid urbanization of America. Immigrants and struggling farmers flocked to these urban areas in search of employment opportunities, fueling the growth of the industrial workforce.
This influx of workers, coupled with the exploitative working conditions prevalent in many industries, resulted in growing poverty and inequality. The stark contrast between the opulence of the wealthy elite and the hardships faced by the working class became a defining characteristic of the Gilded Age.
“It was the best of times, it was the worst of times,” as Charles Dickens aptly described the duality of the Gilded Age, encompassing the immense wealth generated by industrialization and the dire living conditions of the working class.
Amidst this backdrop of socio-economic disparity, labor unions began to arise as a means to combat the injustices faced by workers. Labor unions advocated for better working conditions, fair wages, and other reforms aimed at improving the lives of workers.
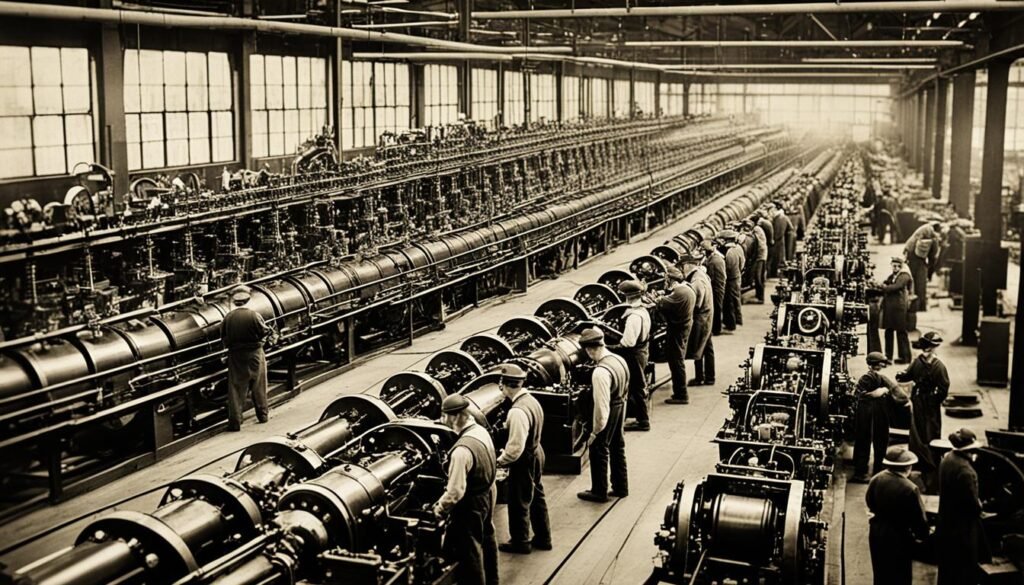
However, these efforts were met with resistance from industrialists who sought to maintain their power and maximize their profits. The struggle between labor unions and industrialists became a significant aspect of the Gilded Age, shaping the trajectory of workers’ rights and labor legislation in the years to come.
Overall, the industrial revolution of the Gilded Age had profound effects on American society. While it brought about rapid economic growth and technological advancements, it also magnified social and economic inequalities. The emergence of cities, the rise of labor unions, and the struggles faced by the working class all played pivotal roles in shaping the landscape of the Gilded Age.
Conclusion
The Gilded Age was a pivotal period in American history, marked by significant economic growth, technological advancements, and the rise of influential individuals and corporations. However, it also brought about profound social and economic inequality, with the working class bearing the brunt of harsh conditions and exploitation.
Despite its challenges, the Gilded Age played a critical role in shaping the future of the United States. It set the stage for the subsequent Progressive Era, where important reforms were implemented to address pressing issues such as income inequality, labor rights, and social justice. The impact of the Gilded Age was far-reaching, driving the transformation of American society and paving the way for future developments.
During this period, the immense wealth accumulated by the likes of Cornelius Vanderbilt, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie contributed to the disparity between the upper class and the working class. However, it is worth noting that some of these industrialists also engaged in philanthropy and supported their communities, leaving behind a complicated legacy.
FAQ
Who are the main cast members of The Gilded Age TV series?
The main cast members of The Gilded Age TV series include [insert names of main cast members].
Can you provide the heights of the characters in The Gilded Age?
The exact heights of the characters in The Gilded Age TV series have not been publicly disclosed.
What are the ages of the characters in The Gilded Age?
The ages of the characters in The Gilded Age TV series vary and are dependent on the storyline and character development.
What was the impact of the Transcontinental Railroad on the United States?
The completion of the Transcontinental Railroad in 1869 led to rapid settlement of the western regions and facilitated easier transportation of goods across the country, contributing to the economic growth of the Gilded Age.
Who were the “Robber Barons” of the Gilded Age?
“Robber Barons” were wealthy individuals, such as Cornelius Vanderbilt, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie, who gained significant wealth and monopolistic power in various industries during the Gilded Age.
How did industrialization impact the Gilded Age?
Industrialization played a major role in the Gilded Age, leading to the emergence of cities and the urbanization of America. However, it also resulted in poverty and inequality, prompting the rise of labor unions advocating for better working conditions and reforms.
What was the significance of the Gilded Age in American history?
The Gilded Age marked a period of economic growth and technological advancements, as well as social and economic inequality. It set the stage for the subsequent Progressive Era, where reforms were made to address issues of income inequality, labor rights, and social reform.

